Behind KANJINTI®
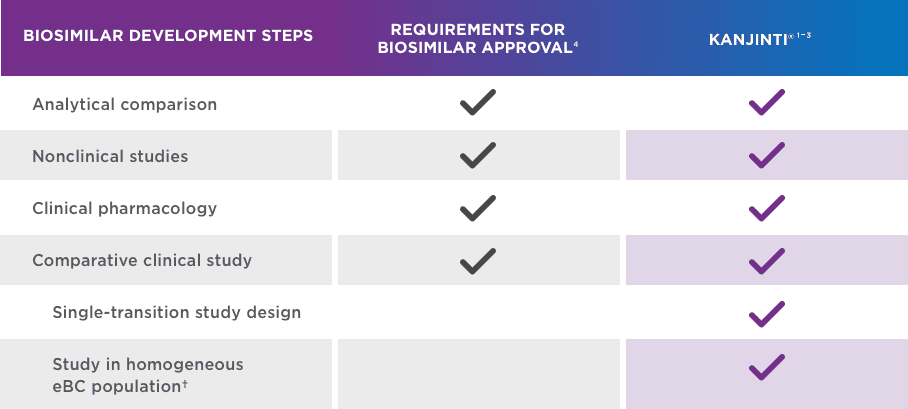
A robust biosimilars program
KANJINTI® IS A PROVEN BIOSIMILAR TO HERCEPTIN®* BASED ON A TOTALITY OF EVIDENCE1-3

FDA-approved for all Herceptin® indications5,6
eBC = early breast cancer.
*EU-sourced Herceptin® was used in the LILAC study. The KANJINTI® clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) study demonstrated equivalence between EU- and US-sourced Herceptin® and KANJINTI®.
†Conducting biosimilar studies in this sensitive population provides scientific evidence supporting use in less sensitive populations.1,7
-
BIOSIMILARITY PROVEN IN A COMPARATIVE CLINICAL STUDY
KANJINTI® WAS PROVEN BIOSIMILAR TO HERCEPTIN®
LILAC study results supported no clinically meaningful differences between KANJINTI® and Herceptin®*
Use of trastuzumab in the neoadjuvant setting is not an approved indication in the product label
for KANJINTI® or Herceptin®. The selection of the patient population was appropriate to support demonstration of no clinically meaningful differences between KANJINTI® and Herceptin®.*1,5,6Study design and key considerations1
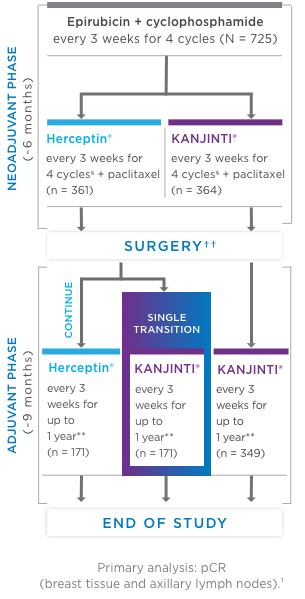
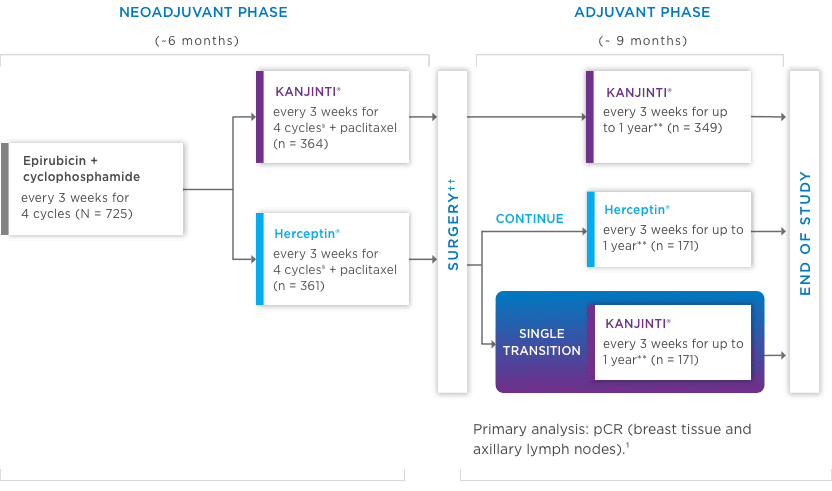
Study population: Patients with early breast cancer (eBC) in the neoadjuvant setting.
- eBC is a homogenous and sensitive population for assessing any clinically meaningful differences between the two products.
Study design: A comparative, randomized equivalence trial between KANJINTI® and Herceptin® in patients with HER2+ eBC (N = 725).
- Prior to surgery, patients received epirubicin (90 mg/m2) + cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) once
every 3 weeks (Q3W) for 4 cycles. Patients were then randomized to KANJINTI®
or Herceptin®, both administered with paclitaxel (175 mg/m2), at a loading dose of 8 mg/kg, then 6 mg/kg Q3W prior to surgery. - Following surgery, patients in the KANJINTI® arm continued treatment with
KANJINTI®; patients in the Herceptin® arm were randomly assigned to either
Herceptin® or KANJINTI®. Treatment continued in all 3 arms Q3W for
≤ 1 year from the initial neoadjuvant dose.
- Prior to surgery, patients received epirubicin (90 mg/m2) + cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) once
every 3 weeks (Q3W) for 4 cycles. Patients were then randomized to KANJINTI®
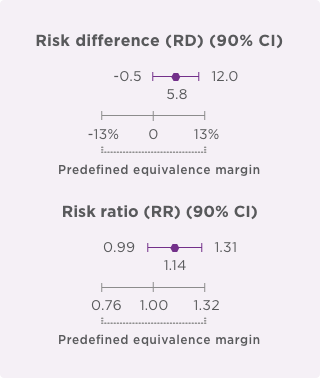
- Coprimary endpoints: Risk difference (RD) and risk ratio (RR) of pathologic complete response (pCR) by local laboratory review evaluated based on the neoadjuvant portion of the study.
CI = confidence interval.
*EU-sourced Herceptin® was used in the LILAC study. The KANJINTI® clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) study demonstrated equivalence between EU- and US-sourced Herceptin® and KANJINTI®.
‡Central laboratory review was performed to reduce the pathologic variability at the local level.
PATHOLOGICAL COMPLETE RESPONSE (pCR) RATES BY CENTRAl LABORATORY REVIEW1,*‡
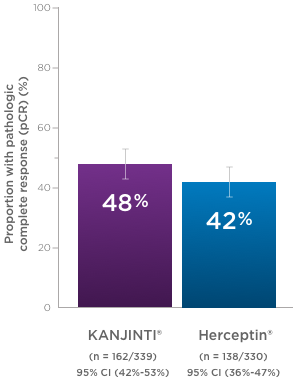
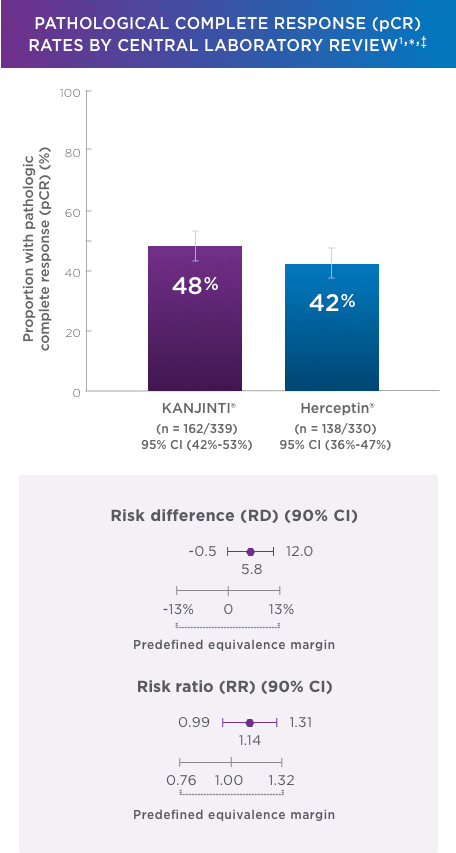
pCR rates by local laboratory review demonstrated similar results1
- In the neoadjuvant setting, 48% with KANJINTI® (95% CI, 43%–53%; n = 172/358) and 41% with Herceptin® (95% CI, 35%–46%; n = 137/338) achieved pCR in both breast tissue and axillary lymph nodes.
- Coprimary endpoints: RD (90% Cl) = 7.3% (1.2%–13.4%); RR (90% Cl) = 1.188 (1.033–1.366).
CI = confidence interval.
*EU-sourced Herceptin® was used in the LILAC study. The KANJINTI® clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) study demonstrated equivalence between EU- and US-sourced Herceptin® and KANJINTI®.
‡Central laboratory review was performed to reduce the pathologic variability at the local level.
KANJINTI® IS THE FIRST AND ONLY HERCEPTIN®* BIOSIMILAR WITH SINGLE-TRANSITION STUDY DATA IN THE eBC SETTING1,5,8-13
Designed to provide robust data by:
- Reinforcing clinical similarity of KANJINTI® and Herceptin®*§
- Reflecting a real-world clinical scenario of transitioning patients from Herceptin®* to KANJINTI®14
- Providing safety and immunogenicity data for up to 1 year of treatment
*EU-sourced Herceptin® was used in the LILAC study. The KANJINTI® clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) study demonstrated equivalence between EU- and US-sourced Herceptin® and KANJINTI®.
§Initial dose of 8 mg/kg IV then 6 mg/kg IV for remaining cycles.
** Total of up to 1 year from the first day of KANJINTI®/Herceptin® administered in the neoadjuvant phase.
††Lumpectomy or mastectomy with sentinel or axillary lymph node dissection.
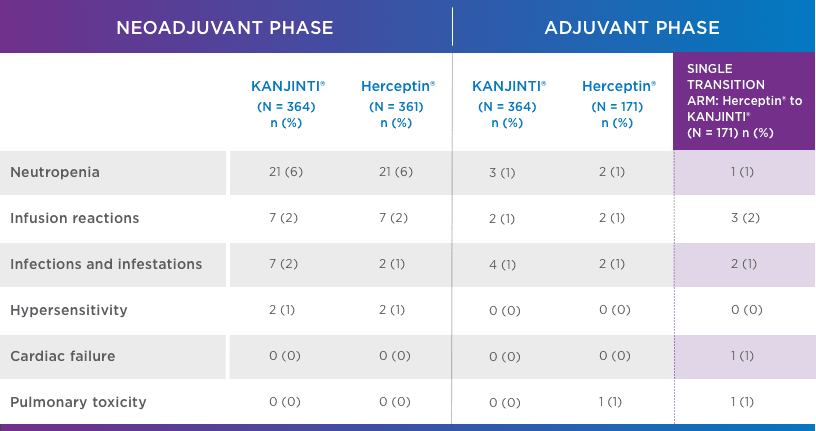
SIMILAR SAFETY AND IMMUNOGENICITY, EVEN IN PATIENTS WHO TRANSITIONED TO KANJINTI®
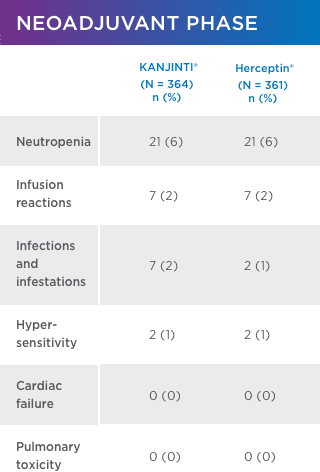
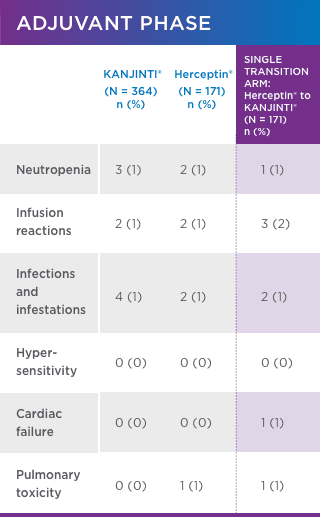
No new or different adverse events (AEs) compared with Herceptin® were observed1
adverse events OF INTEREST (EOI)1 greater than or equal to GRADE 3
CI = confidence interval.
*EU-sourced Herceptin® was used in the LILAC study. The KANJINTI® clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) study demonstrated equivalence between EU- and US-sourced Herceptin® and KANJINTI®.
‡Central laboratory review was performed to reduce the pathologic variability at the local level.
Safety was assessed in both neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings to support biosimilarity. Only treatment-emergent AEs are summarized. For each category, subjects are included only once, even if they experienced multiple events in that category. Following surgery, 171 patients underwent a single transition from Herceptin® to KANJINTI® to further evaluate safety and immunogenicity.
- Antidrug antibody formation was low (≤ 2%) in all study arms. No patients developed neutralizing antibodies.1
- No evidence of increased cardiotoxicity for KANJINTI®—median LVEF values did not change in any study arm over the full course of the study.1
LVEF = left ventricular ejection fraction.
-
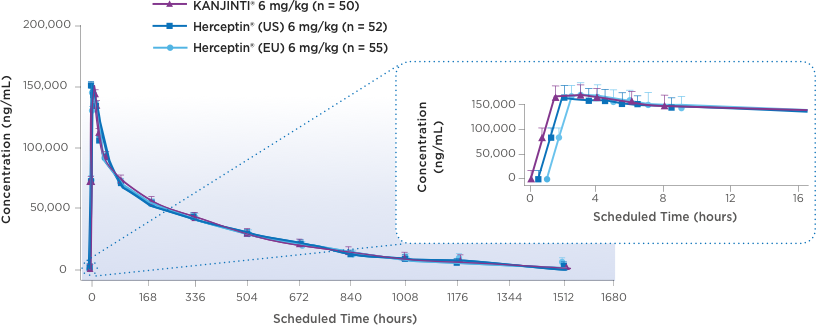
Bioequivalence shown in clinical pharmacokinetic studies
Pharmacokinetics were bioequivalent to Herceptin® in healthy
subjects2,3Mean serum concentration-time profiles for KANJINTI®, Herceptin® (US), and Herceptin® (EU) IN HUman Volunteers2
A randomized, single-blind, single-dose, 3-arm, parallel-group study to determine the pharmacokinetic equivalence of KANJINTI® and Herceptin® in healthy adult males. The primary objective was to evaluate bioequivalence of KANJINTI® and Herceptin® in terms of AUCinf and Cmax (equivalence criteria: 90% CI for geometric mean ratio within 0.80–1.25).2
- The mean serum concentration-time profiles were similar between treatments over the entire course of sampling.2
- Peak concentrations were observed approximately 1.5 to 5 hours after the start of the infusion.2
NO DIFFERENCES IN CLINICAL PK PROFILE
BETWEEN KANJINTI® AND HERCEPTIN®2,3AUCinf = area under the concentration curve versus time from zero to infinity; Cmax = maximum serum concentration; PK = pharmacokinetic.
-
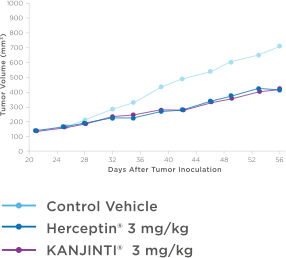
Comparable nonclinical antitumor activity data
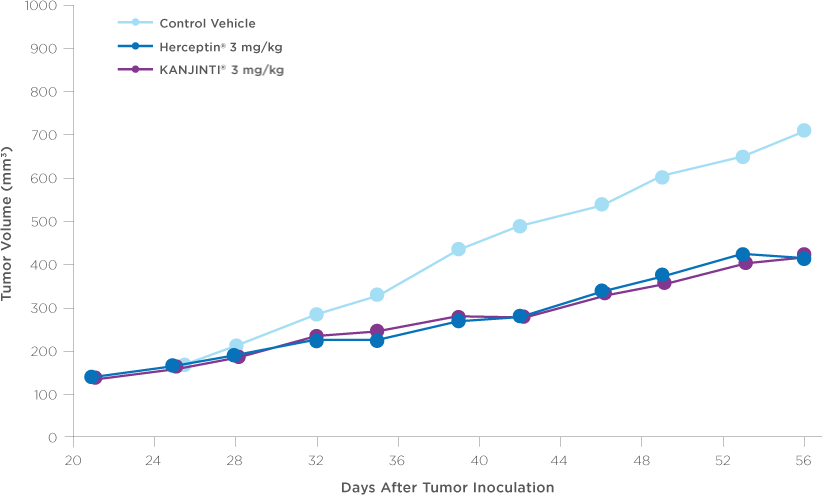
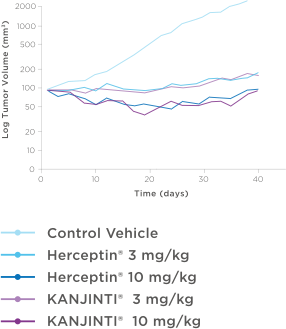
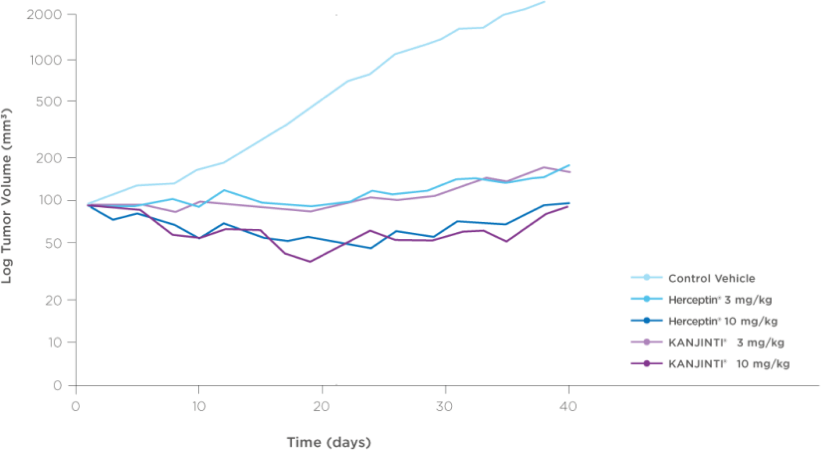
Similar antitumor activity to HERCEPTIN® in XENOGRAFT models3
Antitumor activity in breast cancer xenograft study
NOD/SCID mice were injected orthotopically with BT-474 human breast tumor cells that naturally overexpress HER2 receptors (8 x 106 cells per mouse). After 21 days, treatment with vehicle control, KANJINTI®, or Herceptin® was administered twice weekly by IV for 19 days. Tumor sizes were measured twice per week until day 56.
Antitumor activity in Gastric cancer xenograft study
CD-1 nude mice were injected subcutaneously with NCI-N87 gastric tumor cells (5 x 106 cells per mouse). When average tumor size reached ~100 mm3, vehicle control, KANJINTI®, or Herceptin® was administered twice weekly by intraperitoneal injection for 19 days. Tumor sizes were measured three times per week until day 35.
IN VIVO STUDIES PROVIDE ADDITIONAL
EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT BIOSIMILARITY8BT-474 = metastatic human breast cancer cells; HER2 = human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IV = intravenous; NCI-N87 = human gastric cancer cells; NOD/SCID = nonobese diabetic/severe combined immune deficient.
-
ANALYTICAL (FOUNDATIONAL) STUDIES
Analytical data can be summarized as similar with regard to: DNA sequence, monoclonal antibody protein structure, biological activity, purity, and stability.4